Wave power is a type of hydroelectric power that relies on the capture of energy held by ocean waves. Like wind and solar power, wave power has the potential to be a valuable part of the energy transition.
The potential of wave power lies in the immense amount of kinetic energy at stake. Wave power has far greater energy density than wind or solar. It generates up to 24-70 kW per meter of wave, with peak near-shore power ranging from 40-50 kW per meter. The world’s total wave resource has been estimated to be as much as 2 terawatts (TW) of energy—the equivalent of world’s electricity consumption. T=The annual energy potential off the coast of the United States (U.S.) alone is approximately 2.640 terawatt hours per year, which is equivalent to 65% of U.S. annual electricity consumption.
This content has been archived. It is available through our partners, LexisNexis® and Bloomberg Law.
To view this content, please continue to their sites.
Not a Lexis Subscriber?
Subscribe Now
Not a Bloomberg Law Subscriber?
Subscribe Now
LexisNexis® and Bloomberg Law are third party online distributors of the broad collection of current and archived versions of ALM's legal news publications. LexisNexis® and Bloomberg Law customers are able to access and use ALM's content, including content from the National Law Journal, The American Lawyer, Legaltech News, The New York Law Journal, and Corporate Counsel, as well as other sources of legal information.
For questions call 1-877-256-2472 or contact us at [email protected]
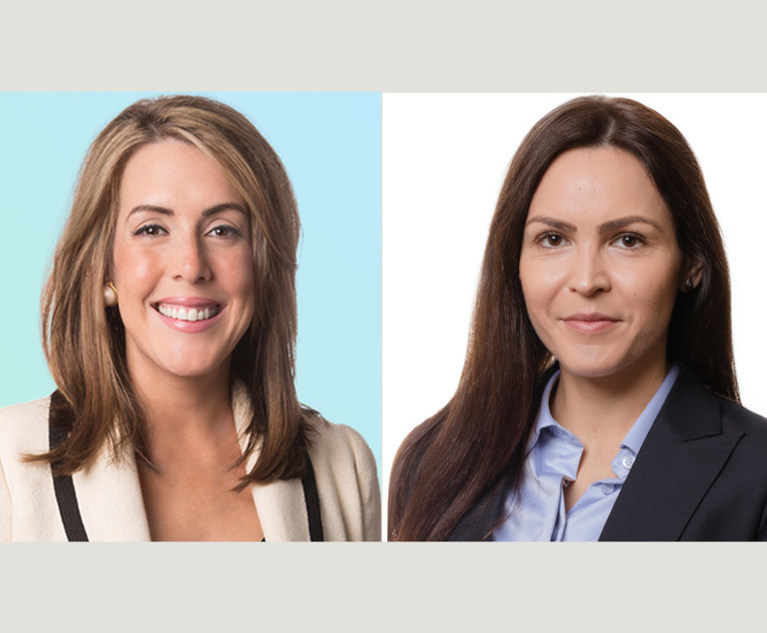
 (L-R) Marcella Burke is an energy attorney and strategic advisor in the Washington D.C. and Houston offices of King & Spalding. Evelina Petraviciute is an associate in King & Spalding’s Corporate, Finance and Investments practice in Abu Dhabi. Courtesy photos
(L-R) Marcella Burke is an energy attorney and strategic advisor in the Washington D.C. and Houston offices of King & Spalding. Evelina Petraviciute is an associate in King & Spalding’s Corporate, Finance and Investments practice in Abu Dhabi. Courtesy photos




